Lab 01 - Introduction
Robotics II
Poznan University of Technology, Institute of Robotics and Machine Intelligence

Laboratory 1: Introduction to Formula Student Driverless Simulator
Back to the course table of contents
1. Formula Student Driverless Simulator
Formula Student is an international series of engineering competitions organized by Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). The contest consists of static and dynamic events. Dynamic events include Skid Pad, Acceleration, Autocross, and Endurance.

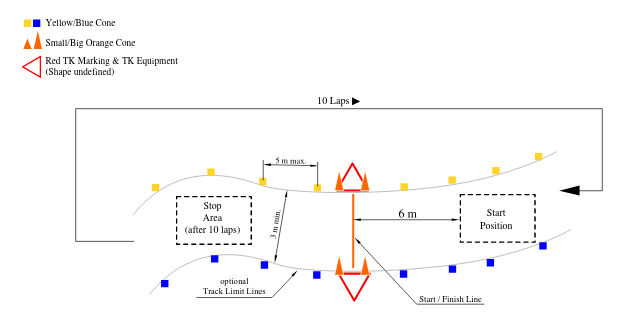
Formula Student Driverless is a dedicated class of Formula Student racecars to autonomous vehicles. This type was launched in 2017 at Formula Student Germany. In Driverless competitions instead of Endurance events, Trackdrive is held. The figure below depicts Trackdrive track marking.
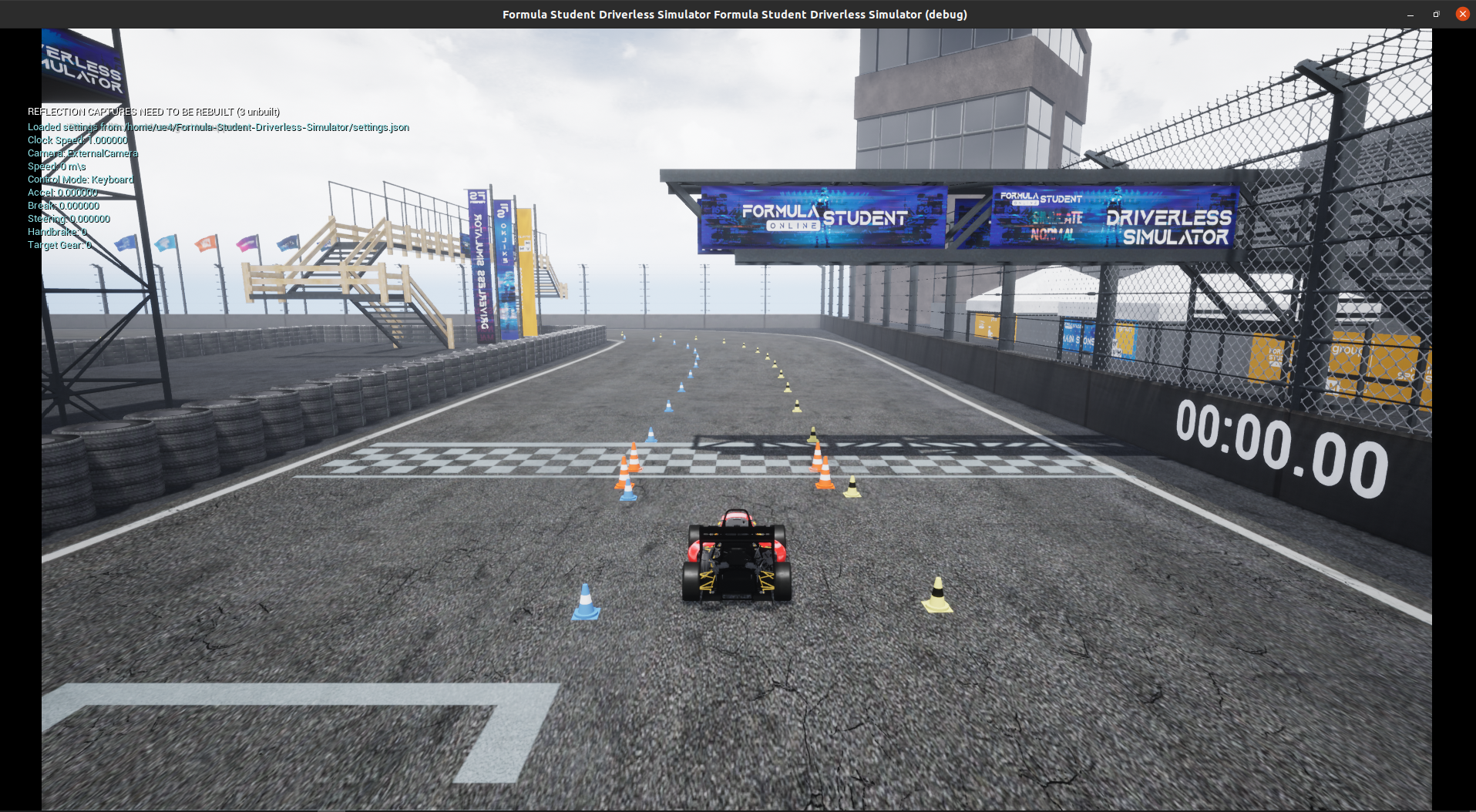
Formula Student Driverless Simulator is a community-based project whose goal was to provide an end-to-end simulation for FS Driverless teams. The simulator was also used in online competitions FS-Online 2020.

Docker image used during laboratories is based on: - Formula-Student-Driverless-Simulator - ROS noetic - NVIDIA docker image with Vulkan and CUDAGL
2. Requirements
2.1. Hardware
* recommended system requirements:
- 8 core 2.3Ghz CPU
- 12 GB memory
- 30GB free SSD storage
- NVidia card with Vulkan support and 3 GB of memory
* testing machine:
- OS: Ubuntu 20.04.1 LTS 64-bit
- Intel® Core™ i5-8400 CPU @ 2.80GHz × 6
- RAM 15.6 GiB
- GeForce GTX 1060 6GB
* docker image size is about 9 GB2.2. Software
- docker >= 19.03
- NVIDIA GPU - nvidia-docker2 section installation on Ubuntu
3. Installation
Important
Check the docker image is available on the registry using
docker imagescommand. If it is, skip to step 3.5.
Option 1 (suggested) - download docker image from docker hub
Download image from cloud or use the following command:
wget "https://chmura.put.poznan.pl/s/52jeTlBwcQY2bIG/download" -O fsds.tarLoad it with the following command:
docker load -i fsds.tarOption 2 - build docker image from scratch
- Clone repository
git clone https://github.com/PUTvision/RoboticsII-FSDS.git- Build docker image from docker directory
docker build -t fsds --network=host -f Dockerfile .3.5 Run
- Add docker access to Nvidia and display
NOTE: This step is required in every new terminal session if it needs to run GUI applications (like simulator, rviz, rqt_plot).
xhost + local:root- Run docker image
NOTE: It is required to change
<STUDENT ID>to your student ID.
docker run \
-it --gpus all --privileged \
--env="DISPLAY=$DISPLAY" \
--env="QT_X11_NO_MITSHM=1" \
--env="NVIDIA_DISABLE_REQUIRE=1" \
--volume="/tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:rw" \
--env="XAUTHORITY=$XAUTH" \
--volume="$XAUTH:$XAUTH" \
--env="NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=all" \
--env="NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=all" \
--network=host \
--name=<STUDENT ID> \
fsds- Get into the running container from another terminal
docker exec -it <CONTAINER ID> bash4. Simulator usage
Simulator
Start simulation calling:
./FSDS.sh -- nosound headless
Robot Operating System
start bridge between FSDS and ROS:
NOTE: this activates the autonomous state and disables keyboard control
roslaunch fsds_ros_bridge fsds_ros_bridge.launch
start rviz with cameras and lidar:
bash roslaunch fsds_ros_bridge rviz.launch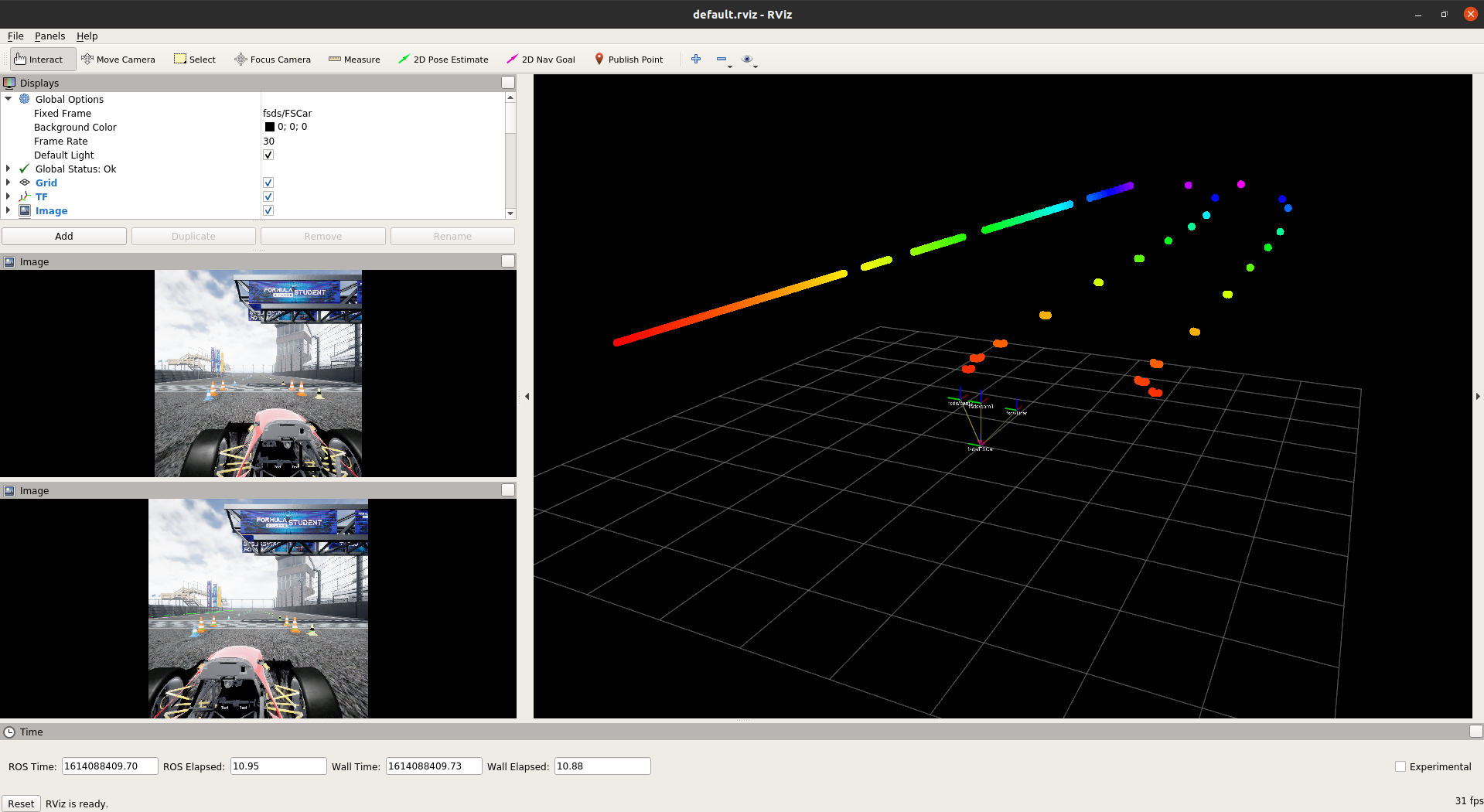
visualize sensors plots:
bash roslaunch fsds_ros_bridge plot.launch
control racecar using gamepad:
NOTE: This is not required for the laboratory. It is only for testing purposes.
roslaunch joystick joystick.launch
5. Prerecorded ROSbags files
NOTE: Rosbags are data files recorded by ROS. They are used to record and play back data from topics. More information about rosbags can be found here.
Recorded rosbag files with test runs on the race track are available here.
6. Tasks
Run container and check if everything works correctly.
Start the simulator, check available maps, and move the racecar using a keyboard.
Connect ROS with simulator using
fsds_ros_bridgepackage and check available topics and services. Then compare the list with documentation.Using
sine_steering.pyscript template fromfsds_roboticsIIROS package (Formula-Student-Driverless-Simulator/ros/src/RoboticsII-FSDSdirectory) implement steering method based on sine signal.
- Build ROS environment calling
catkin buildfromFormula-Student-Driverless-Simulator/rosfolder. - Source environment (
source devel/setup.bash). - Make script executive using
chmod +x sine_steering.pycommand if. - Test your control algorithm on the acceleration map with the command
roslaunch fsds_roboticsII sine_steering.launchand try to move between yellow and blue cones.
TASK
As a laboratory outcome take and add to the eKursy platform two screenshots of:
- simulator acceleration track running
- Rviz viewer with Lidar and Image messages added